|
Antioxidant defense - protection against a ceaseless war!Article submission, Thursday 2nd December 2006 Antioxidant defense is omnipotent to our very existence. If you would, just a imagine a war that rages 24/7, every week, every month of every year for the duration of existence of not just yourself, but for every individual on planet earth. From the moment you are born, your system comes under attack by bacteria, viruses, antigens of all description, not to mention toxins and pollutants and every measurable force imaginable attempting to destroy you. It takes some comprehension of mind to fully appreciate the marvelous mechanism that is our own immune system. However despite this continuing onslaught a healthy supported system will result in very few hick ups and carry on regardless without us ever being aware of what is going on for the duration of life. Why is this? Well we were designed that way, designed to protect ourself from everything within our environment. There is nothing accidental about creation.
However sometimes things can and do go horribly wrong. This war is on all levels, right down to the atomic. Every atom in your body harbours a threat in the form of free radicals, and the problem here being? That there is not one drug can save you from this threat. Only being armed with a little knowledge of good nutrition is the key to hold back this enemy. If we had to pinpoint one singular cause for disease, sickness and indeed aging itself, this is the root of it all.

First of all lets mention that free radical production is normal and part of everyday life and the body has adequate defenses against this, however after saying that the world has changed considerably. Or more accurately we have changed the world considerably to the point where we are now exposed to far more free radical behaviour than our ancestors ever were. We live in a universe that has order to all things on every level. If you remember your school day lessons on physics, atoms are composed of a given numbers of (negative charged) electrons orbiting a nucleus of (positively charged) protons and neutrons (without any charge), with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons. The electrons are involved in chemical reactions as well as binding with other atoms to become molecules.
The number of orbiting electrons governs its behaviour and generally the more it has the more stable (inert) it becomes. One main point is that the electron/proton number must be equal. The problem begins when the number of electrons is not equal (usually less), in which case they become unstable. Should because of a weak bond an atom lose one of its electrons it becomes a free radical. In an attempt to stabilise itself it will attack the closest atom and `steal' an electron in an effort to stabilise itself, that in turn means the `attacked' atom is now unstable and must do the same thus creating a chain reaction. In reality free radicals exist very briefly in time however the cascading (domino) effect can seriously disrupt cell functions and should this happen inside the perimeter of the cell puts the DNA at risk of damage. There are many differing types of free radicals within the body, the ending result of free radical behaviour is what we term oxidation which causes structural fatigue of matter. Much the same as iron that rusts and eventually breaks down in the constant presence of water. There is a definite irony about nature that lends itself to an element(s) in this case oxygen that is not only omnipotent to our existence yet also being very destructive by nature.
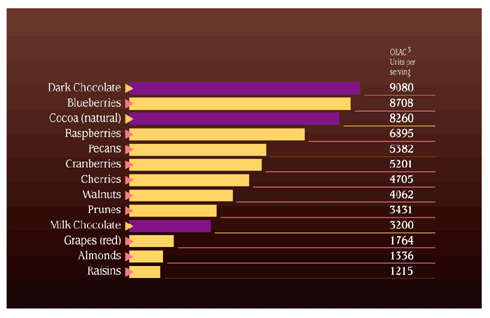
The solution - anti-oxidant defense So what is an antioxidant? Another definition is `against oxidation', these work by protecting structures such as the lipids of the cell walls from structural fatigue. In the main an antioxidant `neutralises' free radicals by donating one of its own electrons which in turn stops the chain reaction continuing. The important fact here is that when an antioxidant gives of its own electrons it does not become unstable and non reactive therefore it breaks the destruction cycle. Antioxidants are manufactured inside the body and are also brought in through our diet. For a cells own defense against this unwanted damage it uses the fat soluble vitamin E, beta-carotene and the co enzyme Q. Of these Vitamin E is considered the most potent antioxidant within the cell membrane. Inside the cell water soluble antioxidant scavengers are present. These include vitamin C, glutathione, peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and catalase.
Antioxidant Essentials Back to Site articles 
|